Diabetology
Diabetes mellitus type 1, type 2 (adult-onset diabetes), type 3 (a rare illness), and gestational diabetes are all under the purview of the medical and scientific field known as "diabetology." The diabetologist's job is to diagnose and treat all forms of diabetes, including type 1 and type 2.
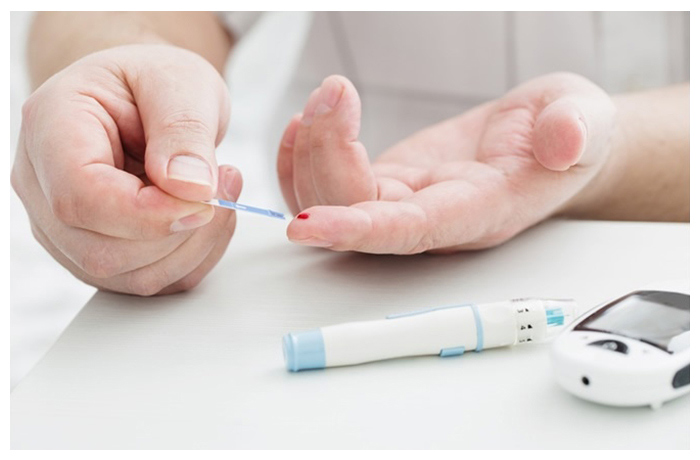
High blood sugar is a symptom of diabetes mellitus, a metabolic disorder. Glucose is transported into cells by the insulin hormone and stored or utilised for energy. The body either doesn't produce enough insulin or can't use the insulin it does produce efficiently in people with diabetes. Diabetes-induced high blood sugar can harm your nerves, eyes, kidneys, and other organs if left untreated.
Diabetology studies all kinds of diabetes along with all the health issues that come along with it. The signs, symptoms, causes, and therapies vary from one kind of diabetes to the next. Sores that do not heal are among the most common symptoms of diabetes, which include increased hunger, increased thirst and weight loss.
Men with diabetes may experience a diminished sex drive, erectile dysfunction (ED), and a lack of physical strength in addition to the more common symptoms of diabetes. Infections of the urinary system, yeast infections, and dry, itchy skin can all be indications of diabetes in women's bodies.
Each kind of diabetes has a unique aetiology. Type 1 diabetes is still a mystery to doctors. Insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas are inappropriately targeted and destroyed by the immune system. Some people's traits are influenced by their genes. An immune system attack can also be triggered by a virus.
Diabetes type 2 can be caused by both hereditary predispositions and one's way of life. Additionally, obesity raises the risk. Your cells become more resistant to insulin's effects on blood sugar if you are overweight, especially in your belly. This disorder is inherited. The risk of developing type 2 diabetes and being overweight is increased among members of the same family who share certain genes.
In pregnancy, hormonal changes lead to gestational diabetes. The placenta secretes substances that lessen the sensitivity of a pregnant woman's cells to insulin. During pregnancy, this might lead to elevated blood sugar levels. Gestational diabetes is more common in pregnant women who are overweight at the time of conception or who gain too much weight during the pregnancy. To conclude, Diabetes can be triggered by both genetic and environmental factors.
Connect with Akshar Hospital to access all these facilities and treatments seamlessly.




